BML-210
BML-210 is a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor with putative effects on leukemia cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. BML-210 is comparable with a well known HDAC inhibitor, phenyl butyrate, in its ability to cause cytotoxic effects dependent on exposure time and dose.
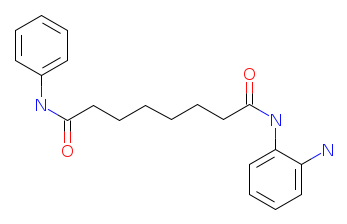
IUPAC Name: N-(2-aminophenyl)-N'-phenyloctanediamide
Molecular Weight: 339.44 g/mol
Molecular Formula: C20H25N3O2
SMILES: Nc1ccccc1NC(=O)CCCCCCC(=O)Nc2ccccc2
Canonical SMILES: C1=CC=C(C=C1)NC(=O)CCCCCCC(=O)NC2=CC=CC=C2N
InChIKey Identifier: RFLHBLWLFUFFDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
CAS Number: 537034-17-6
Melting point: 168-170 °C
Solubility: 10 mg/mL in ethanol; 25 mg/mL in DMSO
2D Molfile: Get the molfile
Synonyms: BML210; N-(2-aminophenyl)-N'-phenyl-octanediamide
BML-210 could be a promising antileukemic agent to induce apoptosis and to modulate differentiation through the modulation of histone acetylation and gene expression.
References:
1) Borutinskaite VV, Navakauskiene R, Magnusson KE. Retinoic acid and histone deacetylase inhibitor BML-210 inhibit proliferation of human cervical cancer HeLa cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Dec;1091:346-55.
2) Savickiene J, Borutinskaite VV, Treigyte G, Magnusson KE, Navakauskiene R. The novel histone deacetylase inhibitor BML-210 exerts growth inhibitory, proapoptotic and differentiation stimulating effects on the human leukemia cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 7;549(1-3):9-18.
3) Herman D, Jenssen K et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors reverse gene silencing in Friedreich's ataxia. Nat Chem Biol. 2006 Oct;2(10):551-8.

|


