Sodium Butyrate
Sodium butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid, is the most common and physiologic member of HDAC inhibitors because it is formed in the colon by fermentation of dietary fibers.
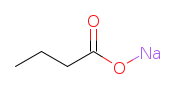
IUPAC Name: Sodium Butanoate
Molecular Weight: 110.08 g/mol
Molecular Formula: C4H7NaO2
SMILES: CCCC(=O)O[Na]
Canonical SMILES: CCCC(=O)O[Na]
InChIKey Identifier: MFBOGIVSZKQAPD-UHFFFAOYSA-M
CAS Number: 156-54-7
Melting point: 250-253°C
Solubility: water (100 mg/ml)
2D Molfile: Get the molfile
Synonyms: NaB, SB, NaBu, Butanoic acid sodium salt, Sodium propanecarboxylate
Sodium butyrate is able to induce cell cycle arrest, differentiation and apoptosis in various cancer cells. The compound in millimolar concentrations causes an accumulation of acetylated histone species in a variety of vertebrate cell lines.
References:
1) Bandyopadhyay et al. Overexpression of Histone Deacetylase 1 Confers Resistance to Sodium Butyrate–Mediated Apoptosis in Melanoma Cells through a p53-Mediated Pathway. Cancer Research 64, 7706–7710, November 1, 2004
2) Sawa H, Murakami H, Ohshima Y, Sugino T, Nakajyo T, Kisanuki T, Tamura Y, Satone A, Ide W, Hashimoto I, Kamada H: Histone deacetylase inhibitors such as sodium butyrate and trichostatin A induce apoptosis through an increase of the bcl-2-related protein Bad. Brain Tumor Pathol 2001, 18:109-14.
3) Candido EP, Reeves R, Davie JR. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105-13.

|


