
 |
|
| Home | Vorinostat | CI-994 | MS-275 | BML-210 | M344 | NVP-LAQ824 | Panobinostat | Mocetinostat | PXD101 | Trichostatin ATrichostatin A (TSA) is an organic compound that inhibits both class I and II HDACs (histone deacetylases). TSA has potent dose-dependent antitumor activity against breast cancer in vitro and in vivo, strongly supporting HDAC as a molecular target for anticancer therapy in breast cancer. 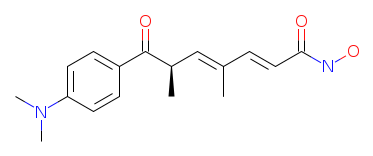
IUPAC Name: (2E,4E,6R)-7-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl-7-oxohepta-2,4-dienamide TSA suppresses the activity of HDAC leading to an increase in histone acetylation. This histone acetylation induces an enhancement of the expression of specific genes that elicit extensive cellular morphologic and metabolic changes, such as growth arrest, differentiation and apoptosis. Trichostatin A has been shown to induce apoptosis in many cancer cells at submicromolar concentrations with very low toxicity toward normal cells. References: |
| CBHA | PCI-24781 | ITF2357 | Valproic Acid | Trichostatin A | Sodium Butyrate | |
|
© 2010-2019 www.hdacis.com |